N Terminal Modification
N-terminal modification can reduce the overall charges of peptides.
QYAOBIO has advanced peptide modification capability, we provide more than 300 types of N-terminal modifications for various research requirements. Normally, chemically synthesized peptides have free amino-terminals, acetyl modifications can remove charge from the amino terminus. Then create the closer peptide mimics with native charge state.
The N-terminus allows more modifications quite easily, while C-terminal modification is more challenging. The peptide modifications can modify properties of peptides, this is hardly predictable and requires systematic testing.
N-terminal modification Necessity
Post-translational modifications are characteristic of secretory or cell-surface proteins, most proteins undergo modifications whatever the cellular desination.
N-terminal modification can reduce the overall charges of peptides, then reduce the overall solubility. Furthermore, N terminal modification will increase peptide stability, as this modification generates a mimic of the native proteins. Therefore, this modification method will increase the bio-activity of peptides and prevent enzyme degradations.
Classification of N-terminal Modifications
Acetylation
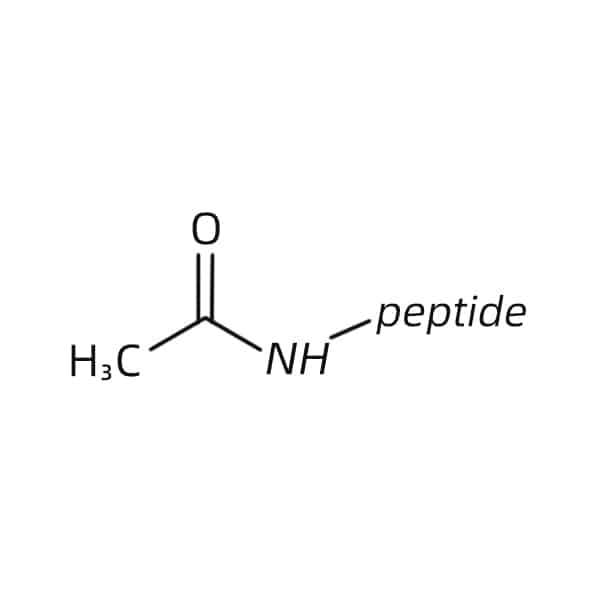
Acetylation on N-terminus will remove positive charge on peptides, and assist peptides to imitate natural structure. In addition, this modification will also increase peptide stability towards enzymatic degradation from exopeptidases.
Dansyl
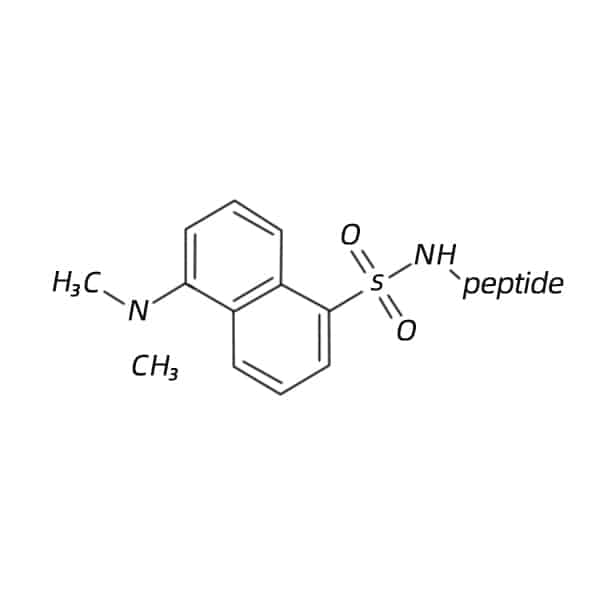
Dansyl labeled peptides are applied in fluorescence-based assays with excitation/emission wavelength of 342 nm/562 nm.
DNP (2, 4-Dinitrophenyl)
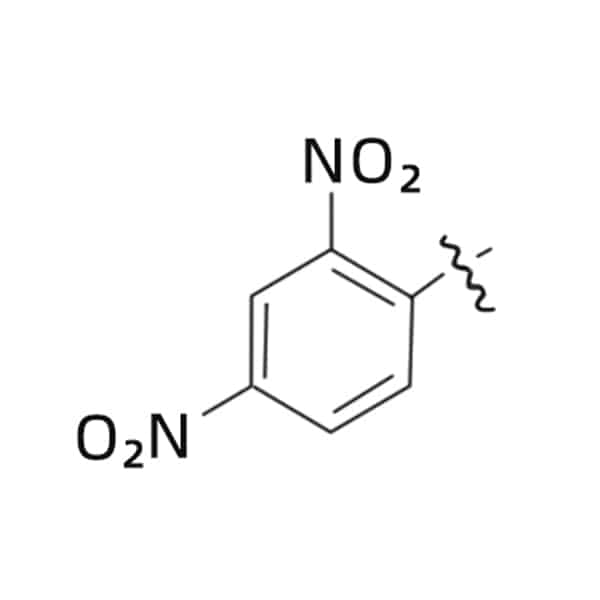
DNP are normally applied as a quencher for MCA or tryptophan. This modification can be attached to the N-terminus of peptides, or lysine side chain as an internal modification. The common wavelength of excitation is 354- 400 nm.
KLH & BSA
Normally, the peptide can couple to carrier proteins, like KLH, or BSA. Carrier proteins conjugate to the N- or C- terminus of peptides through an inserted N- or C-terminal cysteine. KLH or BSA coupled peptides are applied for immunization to increase the cell-mediated immune response.
MCA (7-Methoxycoumarinyl-4-acetyl)
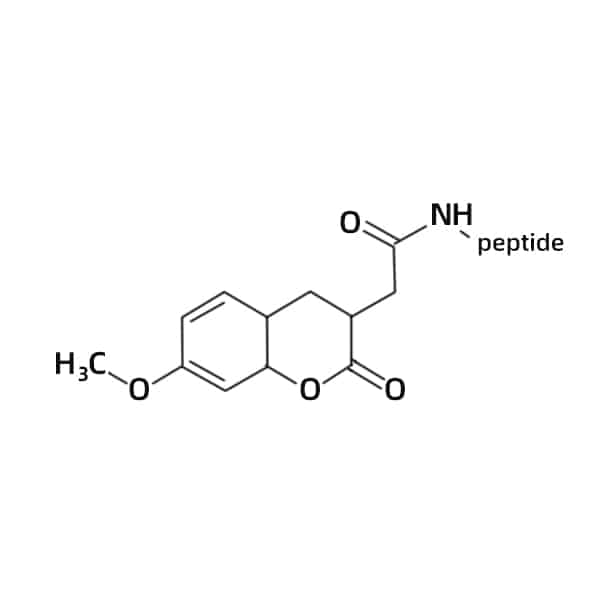
MCA labeled peptides are applied in localization of protein-protein interaction and application, the wavelength of excitation/emission are 325/392 nm.
FITC (Fluorophoreisothiocyanate)
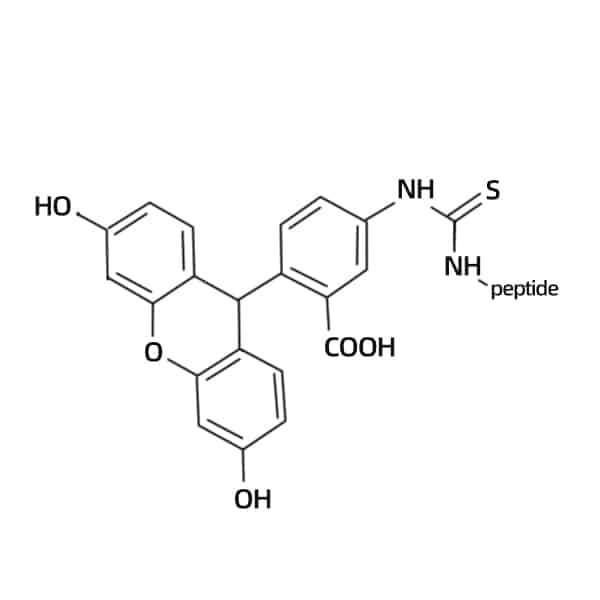
FITC can conjugate to the peptides at the N-terminus through the aminocaproic acid (Ahx) linker. Furthermore, an aminohexanoyl spacer is inserted between the fluorophore and the peptides for effective N-terminal labeling. The excitation/emission wavelength are 490/520 nm.
Biotin
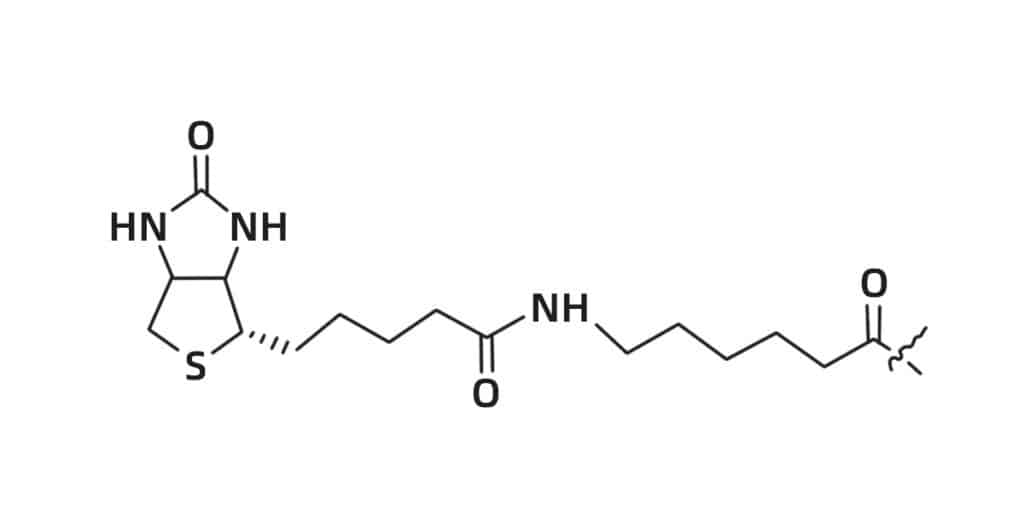
As biotin has strong affinity for both streptavidin and avidin, the biotinylation of peptides is an effective technology for specific peptides binding to streptavidin-coated surfaces. Peptide biotinylation can be synthesized at both N- or C- terminus. Biotin couple directly to N-terminal primary amino group. Biotin-labeled peptides are normally applied in immunoassays, histocytochemistry, and fluorescence-based flow cytometry.
Fatty Acid
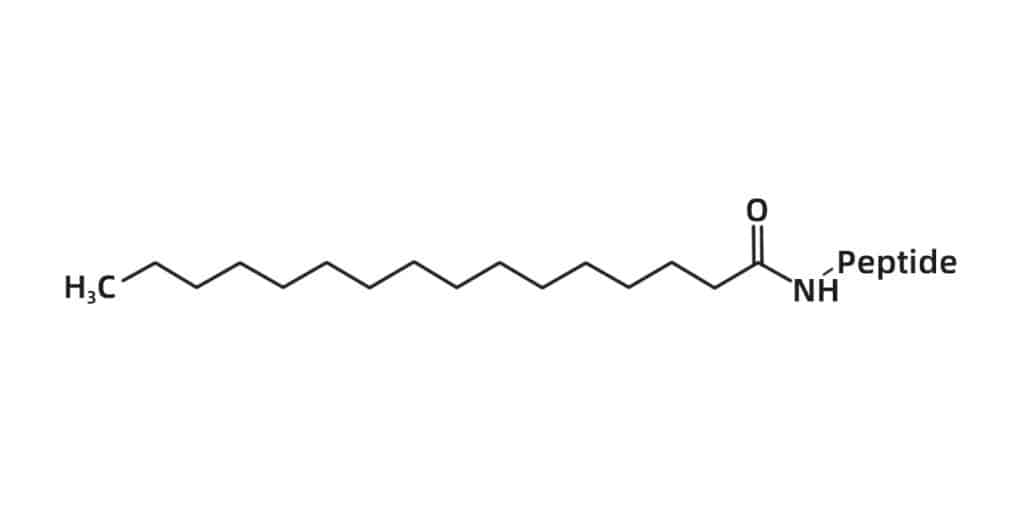
Peptide binding with fatty acid at N-terminus will increase the cell permeability of peptides, and assist the bind to cell membranes. The common peptide fatty acid modifications including: caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), lauric acid (C12), myristic acid (C14), palmitic acid (C16), stearic acid (C18).
Palmytoyl
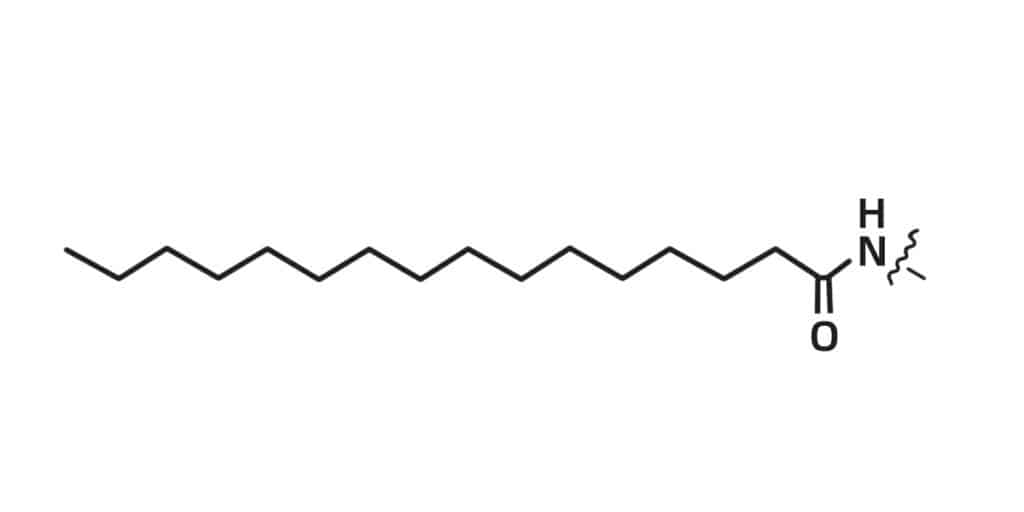
Palmytoylated peptides can increase the cell permeability of peptides, and increase binding ability of peptide to cell membrane.
Qyaobio has excellent experience in custom peptide synthesis of N-terminal modification, we provide confidential and efficient service at competitive price. Every synthesis step is subject to our stringent quality control.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
