Glycopeptides
Glycopeptides are attractive substrates for therapeutic drug development.
Glycopeptides are a class of glcosylated or nomribosonal peptides. Peptides and proteins are attractive substrates for therapeutic drug development, for the reason of exquisite target specificity and low toxicity profiles. However, complex structures of peptides and proteins also result in several challenges in solubility, stability, aggregation, low bio-availability, and poor pharmacokinetics. Therefore, numerous chemical strategies are developed to address these issues by introduction of natural or non-natural modifications. Such as glocosylation, lipidation, cyclization, and PEGylation.
Glycosylation is one of the most useful modifications of peptides, as its contribution to increase stability, improve solubility, and extend circulation half-lives of bio-molecules. But cellular glycosylation as a highly complex process results in heterogenous glycan structures, this confounds quality control in chemical or biological assays. Therefore, chemical glycosylation methods are critical to acquisition of homogenous glycopetides, and expand the possibility of glycopeptide drugs. Our core glycosylation technologies are solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and chemoenzymatic process.
Glycosylated Peptides
Sugar moieties can be incorporated into custom peptides at single or multiple locations, in order to create glycosylated or glycated peptides. Glycosylation has considerable physiological and biological effects on stability, folding, solubility, trafficking, immuno-genicity, and cell growth, adhesion, interactions.
Glycosylation
Glycosylation is the most abundant chain modification of peptides in nature, Glycoproteins are the significant class of therapeutic targets and clinical biomarkers. Glycosylated peptides are involved in intra-cellular communication as the most important recognition signals, such as apoptosis, cell growth regulation, infection process, and immunological differentiation.
Glycosylation is the most frequent post-translational modification in peptides and proteins in eukaryotic cells. Glycosylated peptides and proteins play the key roles in cell-signaling, such as cell adhesion, cell infections. In addition, glycosylation also can affect the protein characteristics like stability and reduction of antigenicity.
Depending on the site of peptide glycosylation, there are two main classification of glycosylated peptides: N-linked glycopeptides, O-linked glycopeptides. The N-linked glycosylation is more frequent, while O-linked glycosylation has more diversification. Glycosylation usually occurs on the side chain of Ser, Thr and Asn, but other amino acids can be glycosylated as well. The different sugar entities are as following:
- Glucose (Glc)
- Galactose (Gal)
- Acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc)
- N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc)
- Fucose (Fuc)
- Mannose (Man)
This sugar entities exert diverse impacts on the conformation of peptides. In addition, the position of glycosyl units also affect the biological properties of modified peptides. QYABOBIO will assist you to develop the glycopeptides in different applications.
Classification of Glycosylation
According to the glycosidic linkage between the amino acid and the sugar, peptide glycosylation is classified into four main categories:
- N-linked glycosylation
- O-linked glycosylation
- C-Mannosylation
- Glycophosphatidlyinositol (GPI) anchor attachments
Glycopeptides (glycosylated peptides) are normally divided into two principal classes:
N-linked Glycopeptides
- N-linked glycopeptides are the most frequent glycopeptides, these peptides contain the N-glycosidic bond between a glycan and the side chain of Asp.
- The site of N-glcosylation in N-glycopeptides are characterized by sequons Asn-Xaa-Ser/Thr (Xaa is any amino acid except proline).
- There are more variable in the carbohydrate moiety, including alpha- and beta-Glc, beta-N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc).
O-linked Glycopeptides
- O-linked glycopeptides have far more diversification than N-linked glycopeptides. The most abundant is the mucin-type with an α-linkage beyweeen GalNAc and serine or threonine.
- Other saccharides link to serine and threonine including: α-galactose(Gal), glucose(Glc), fucose(Fuc), mannose(Man), and xylose(Xyl).
- O-GlcNAc modification is a separate class of O-linked glycosylation, because of its functional distinct. This classification is found as monosaccharides attached to either Ser or Thr.
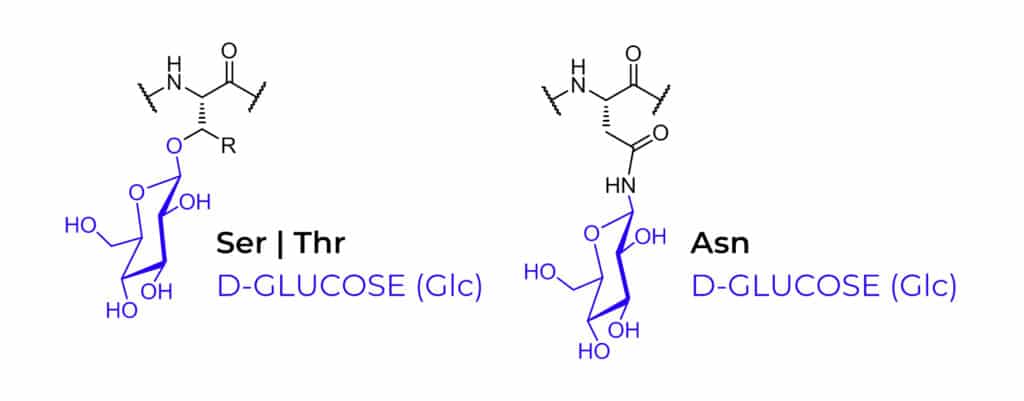
Glycosylation is the most common post-translational modification of peptides or proteins in eukaryotic cells. The carbonhydrate portions of glycopeptides show a large diversity and have critical roles in recognition signals of intracellular communication. Such as cell adhesion, cell-growth regulation, infectious processes, and immunological differentiation.
Advantages of Glycosylated Peptides
The glycosylated peptides has various advantages as following:
Glycosylated Amino Acids
The following table list the selection of glycosylated and glycated amino acids for custom peptides’ incorporation. Other glycosylaton options are also available for personal request, our professional technical team will evaluate the appropriate starting materials and available synthesis procedures.
Glucose
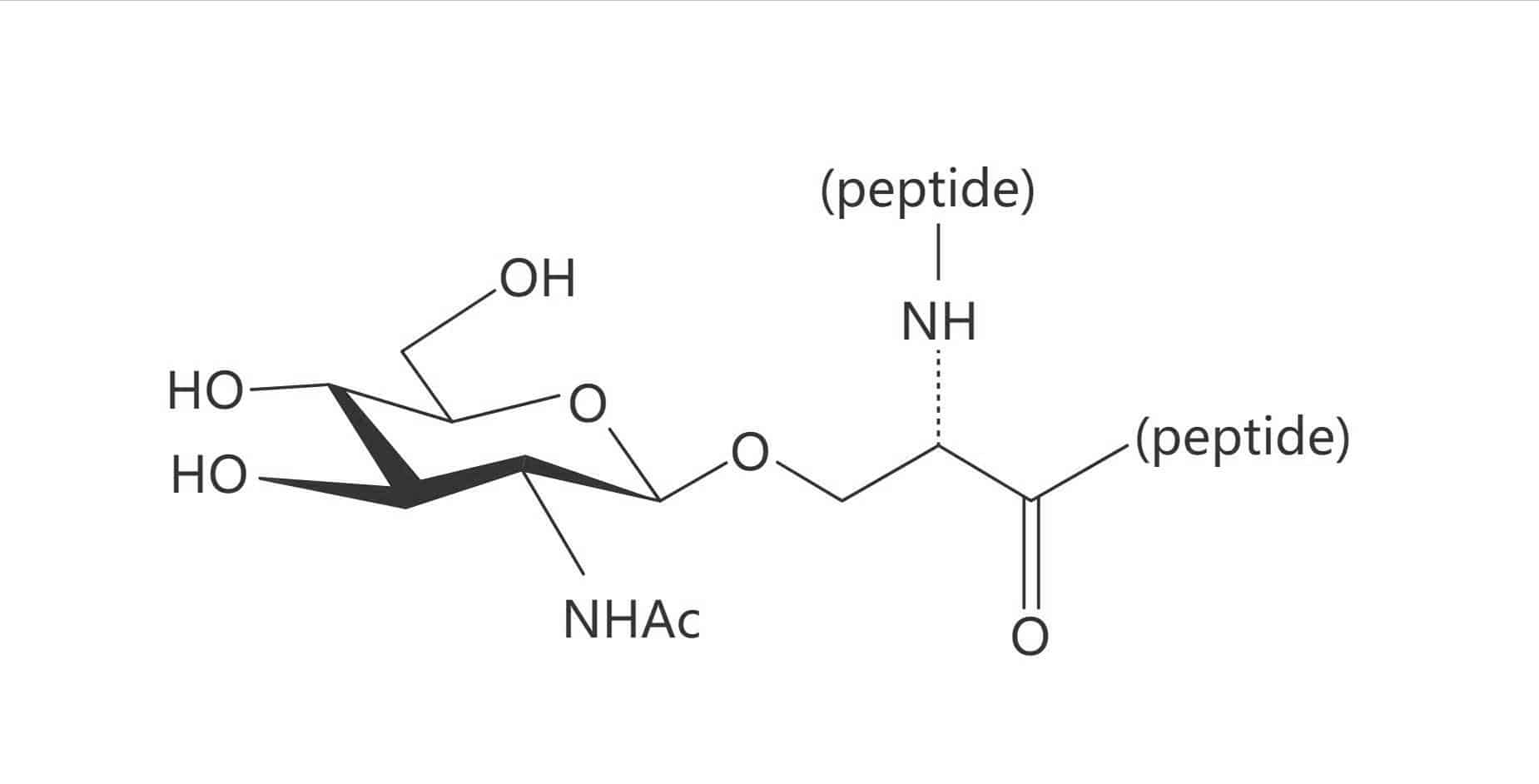
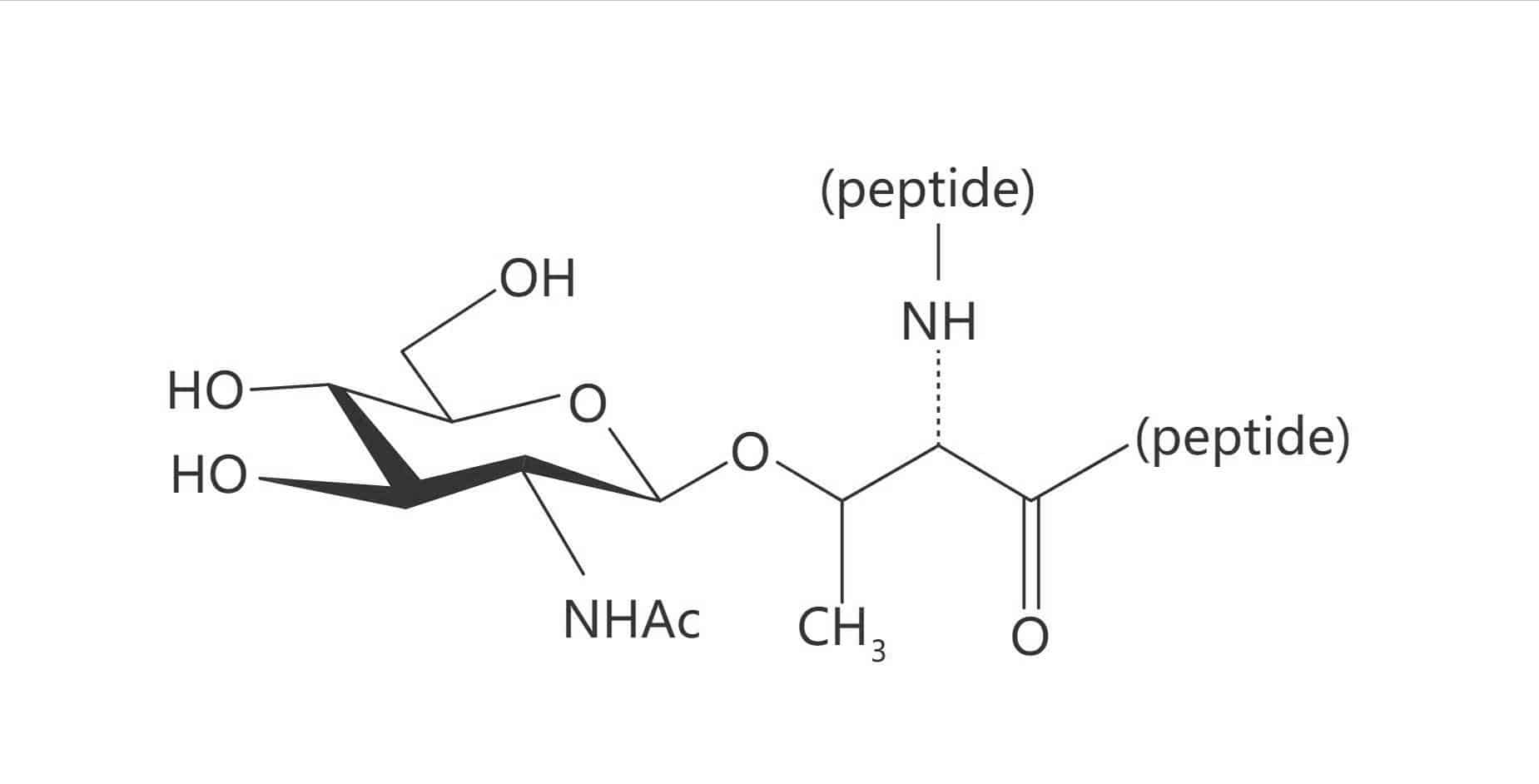
Ser(β-D-GlcNAc)
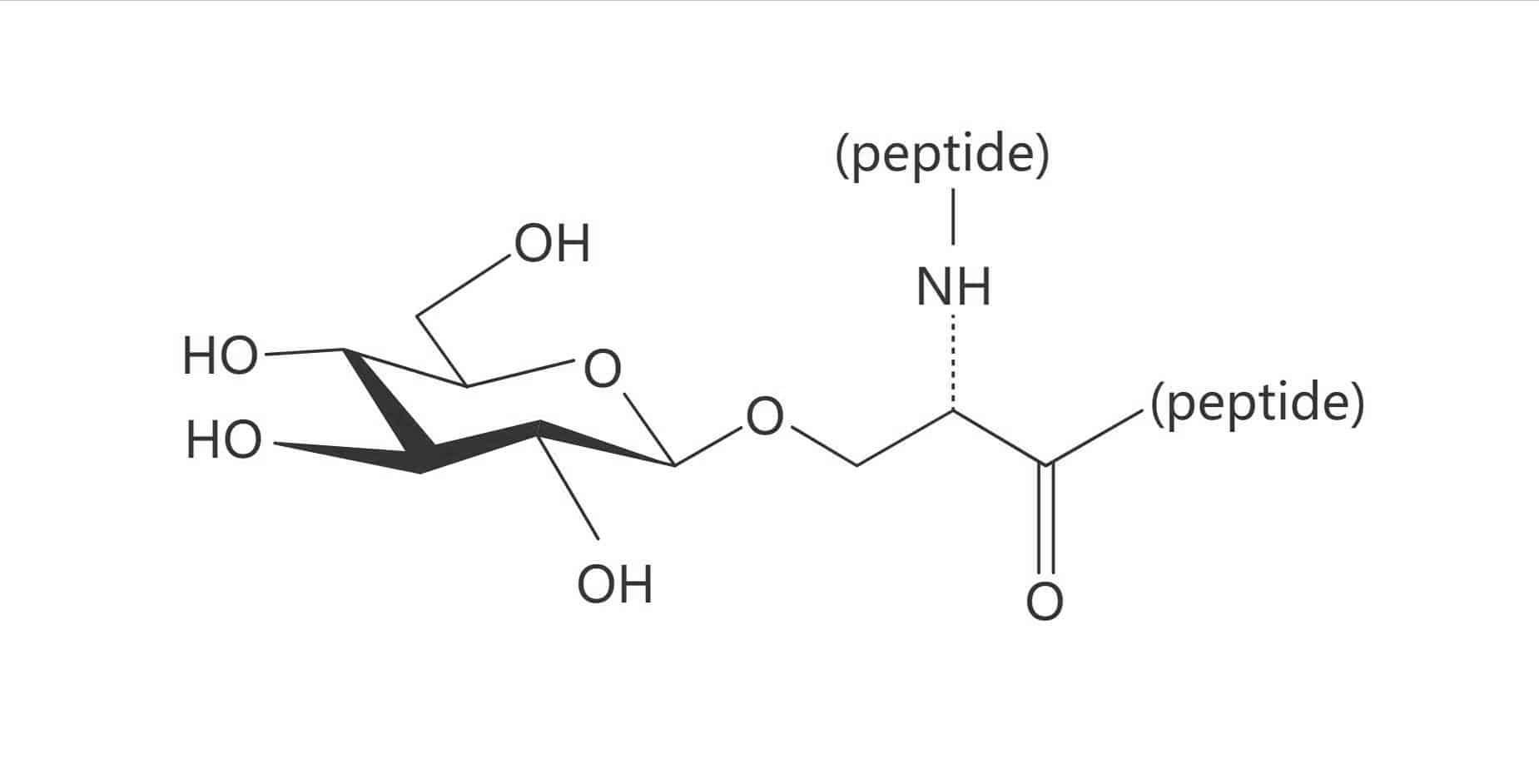
Ser(β-D-Glc)
Thr(β-D-GlcNAc)
Thr(β-D-Glc)
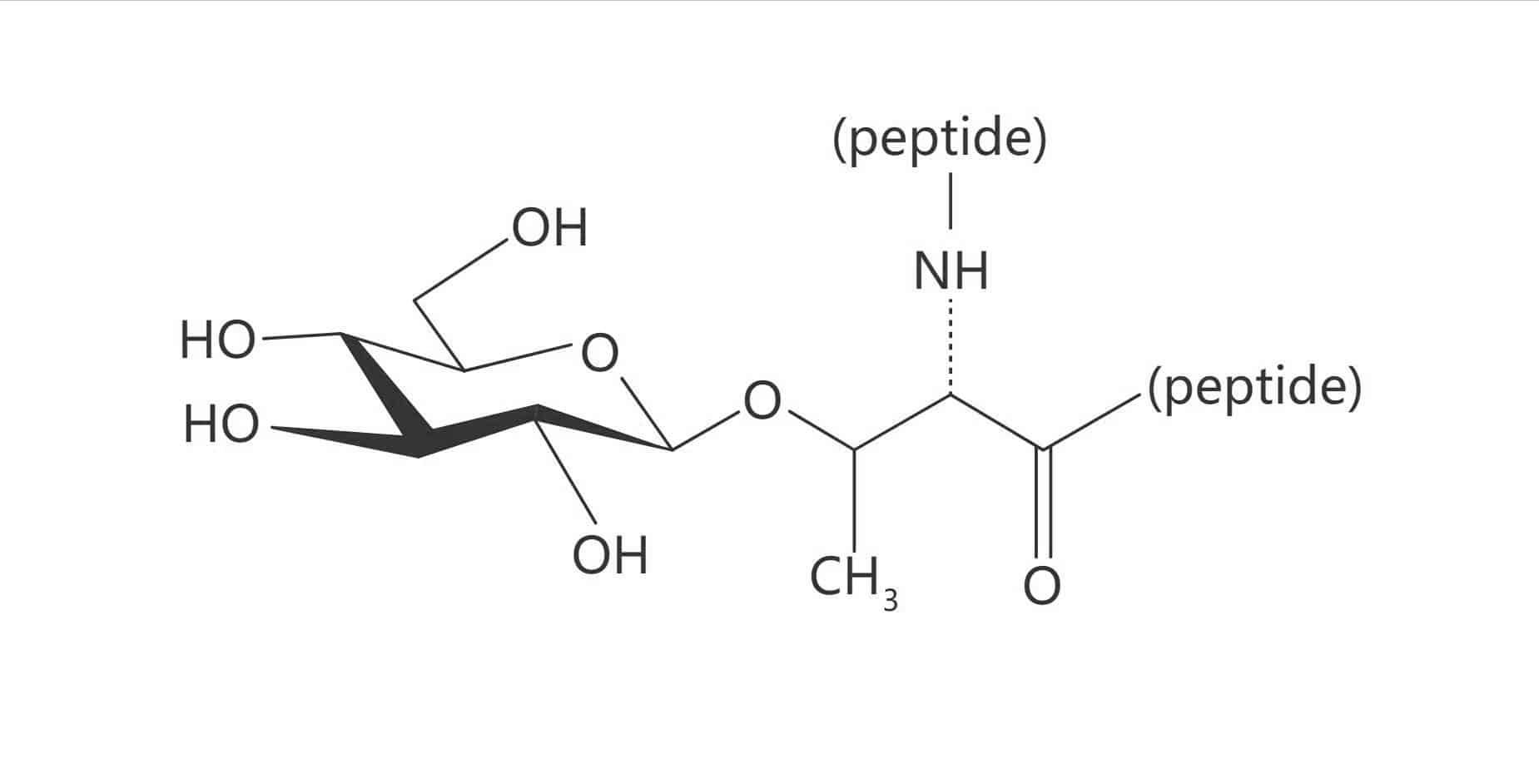
Asn(β-D-GlcNAc)

Asn(β-D-Glc)
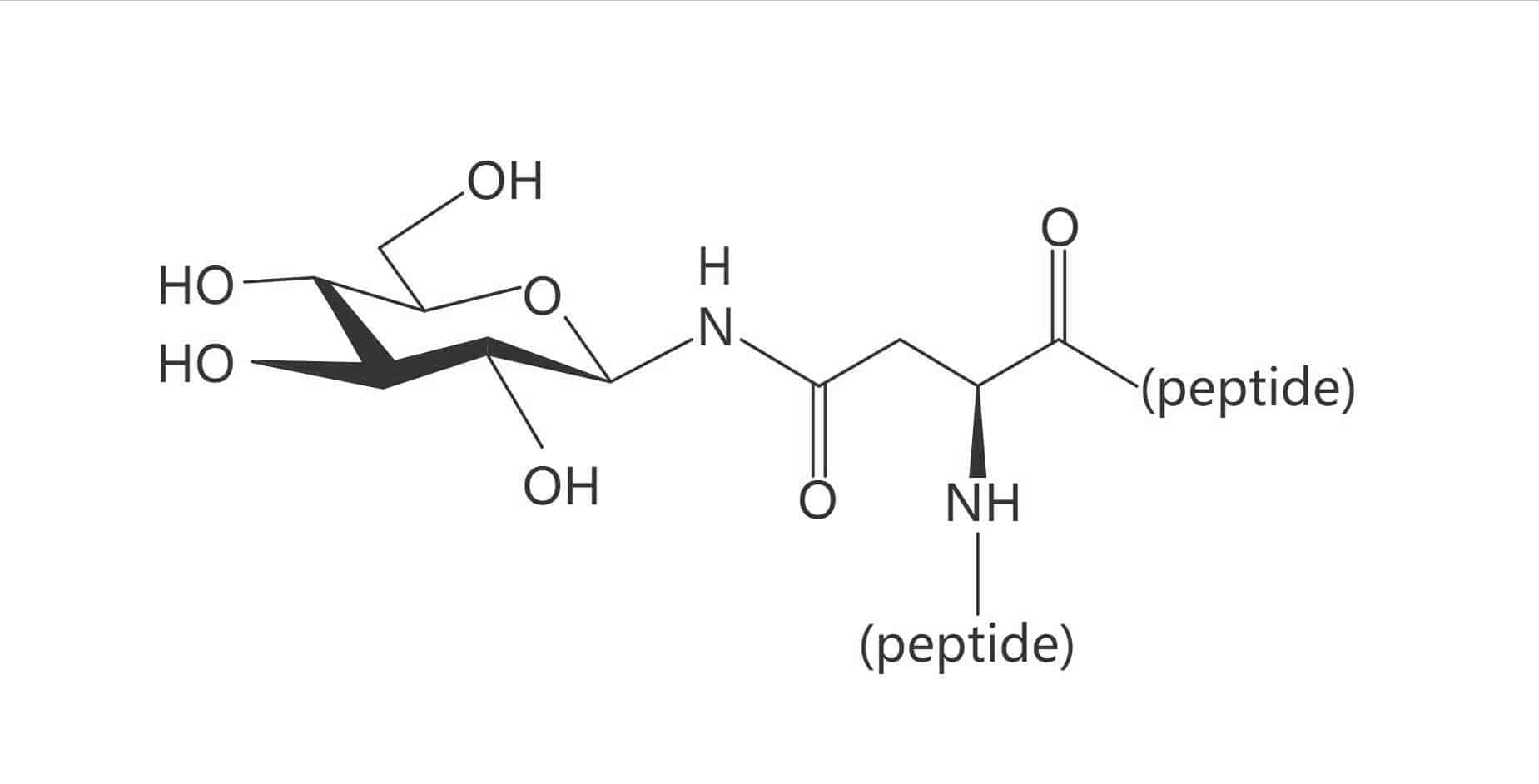
Galactose
Ser(α-D-GalNAc)|(Tn Antigen)
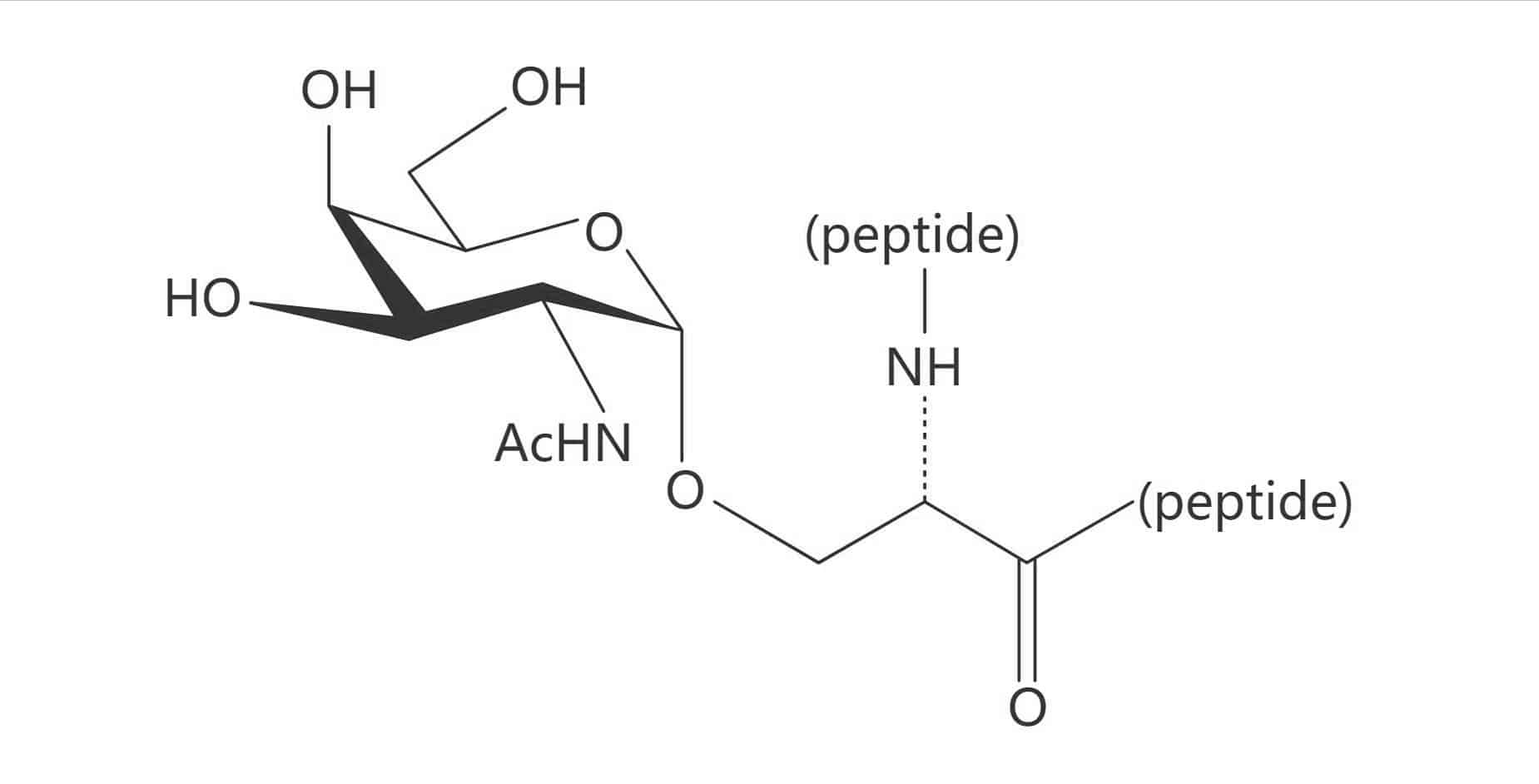
Ser(α-D-Gal)
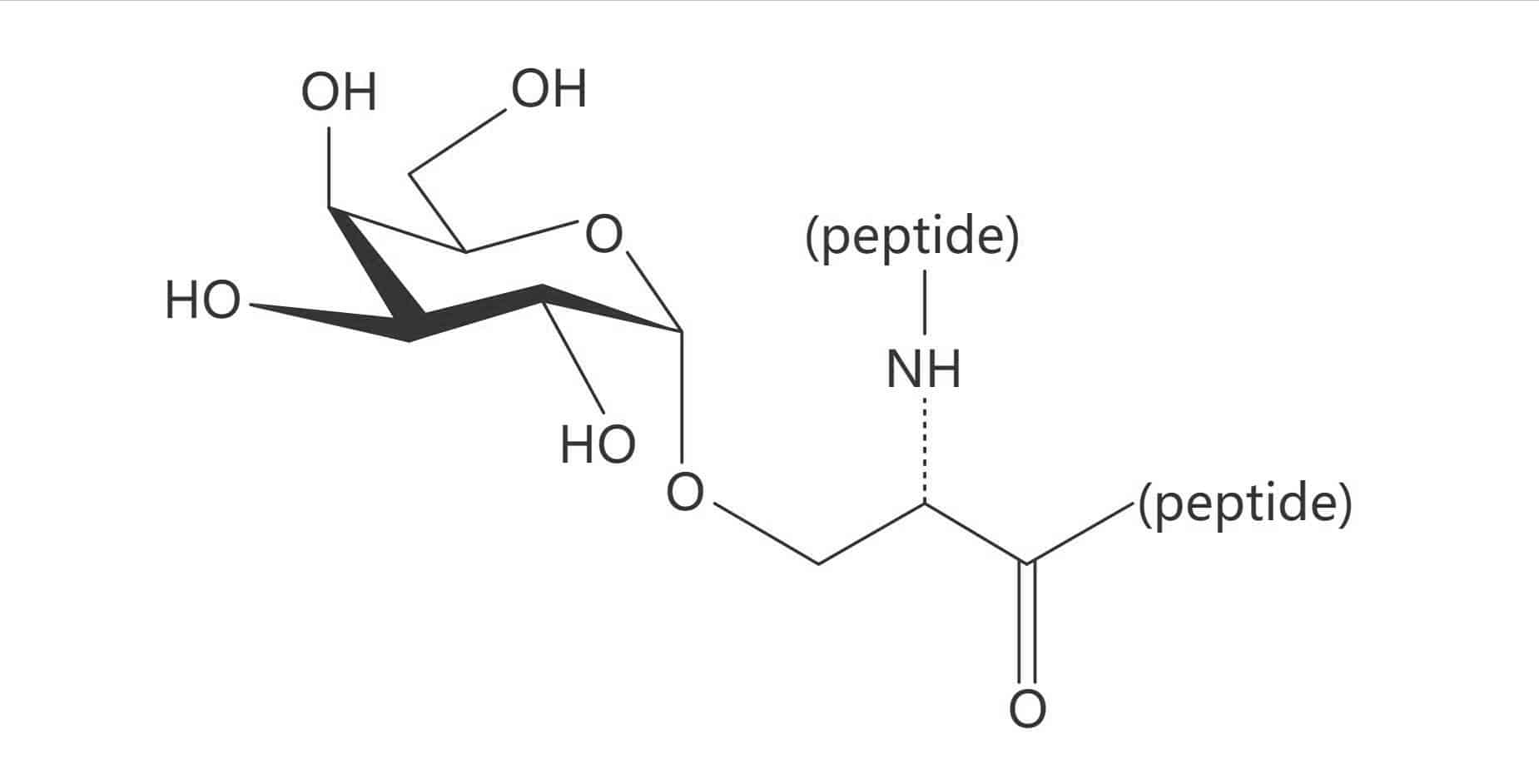
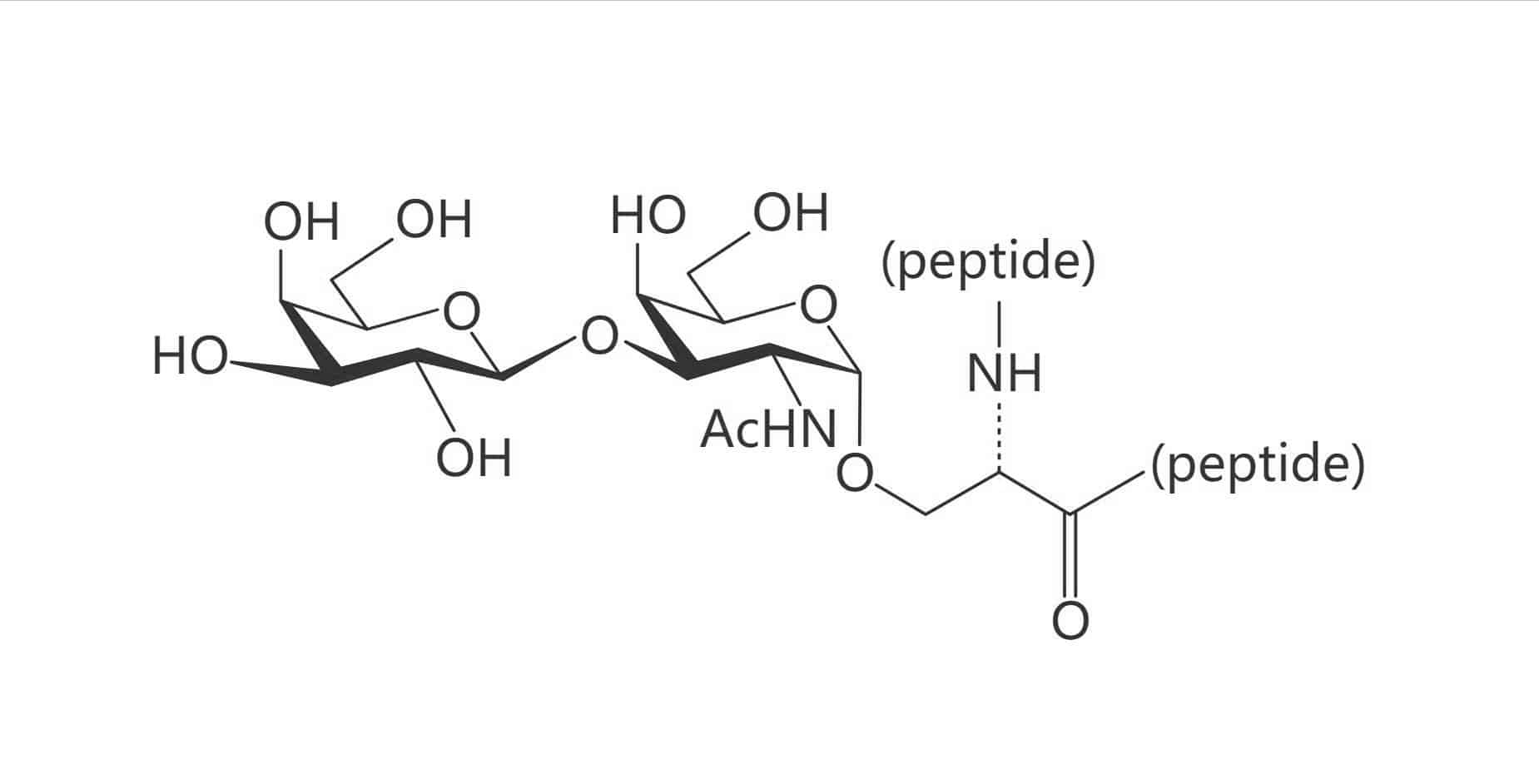
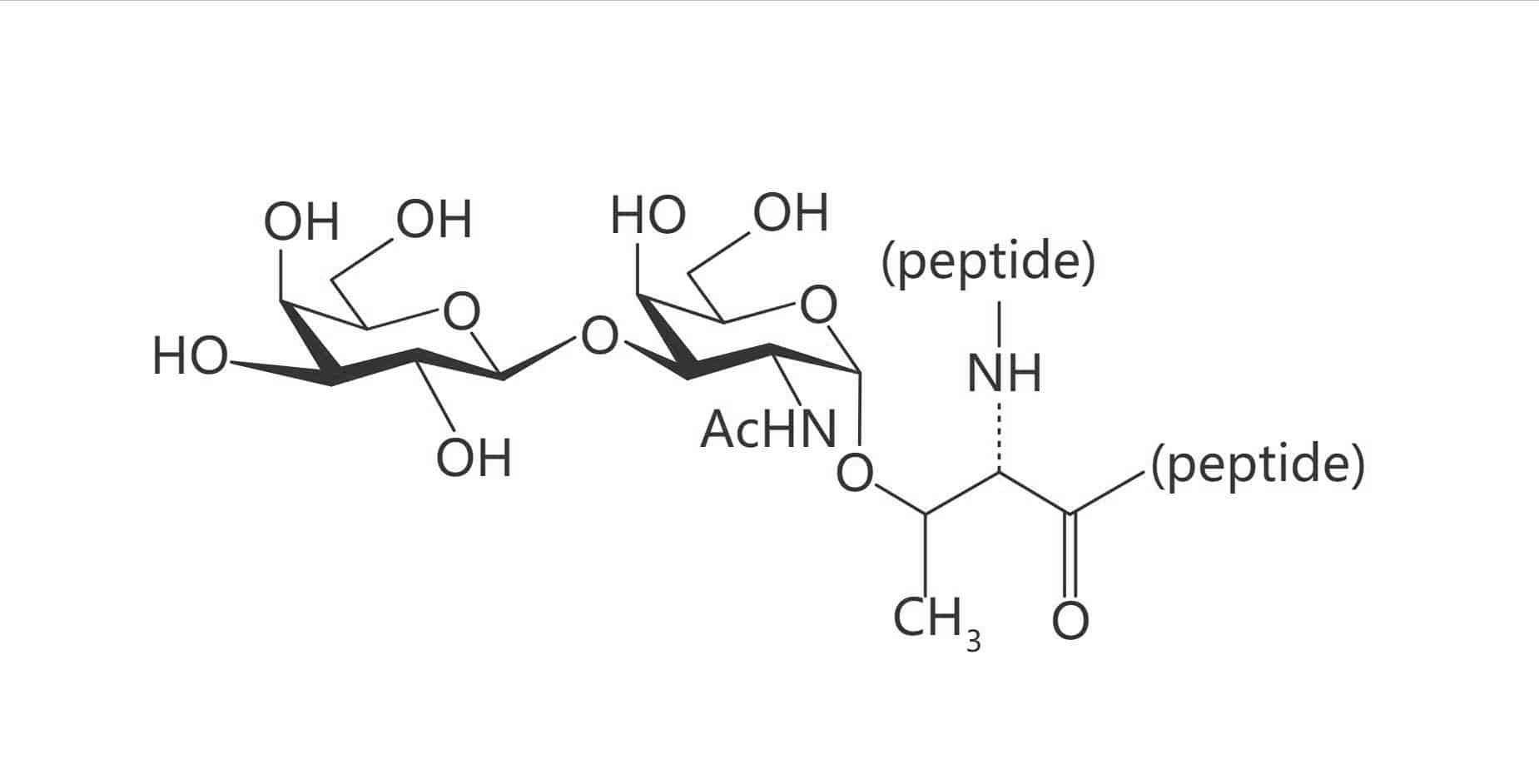
Ser(Gal β(1-3) GalNAc)|(TF Antigen)
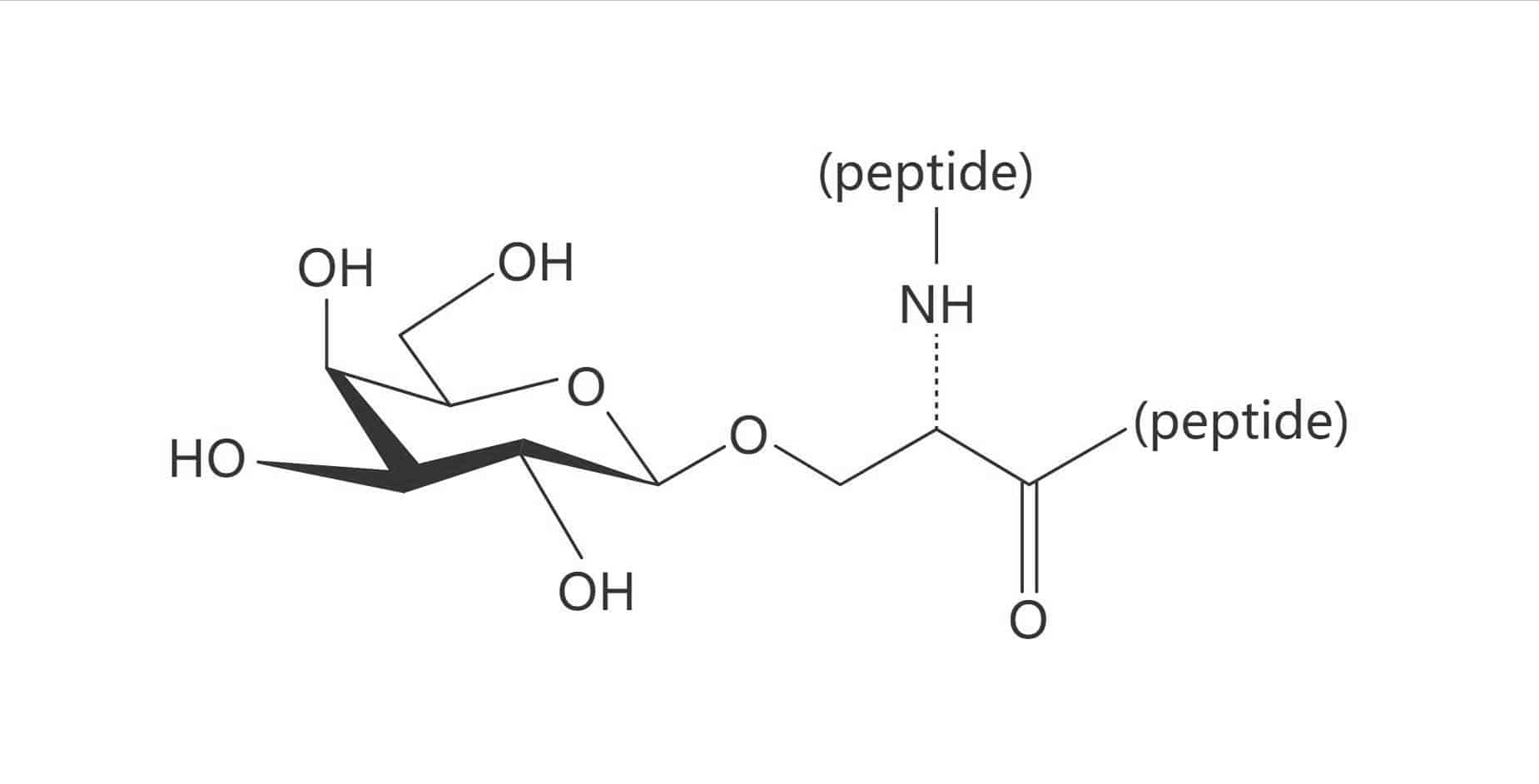
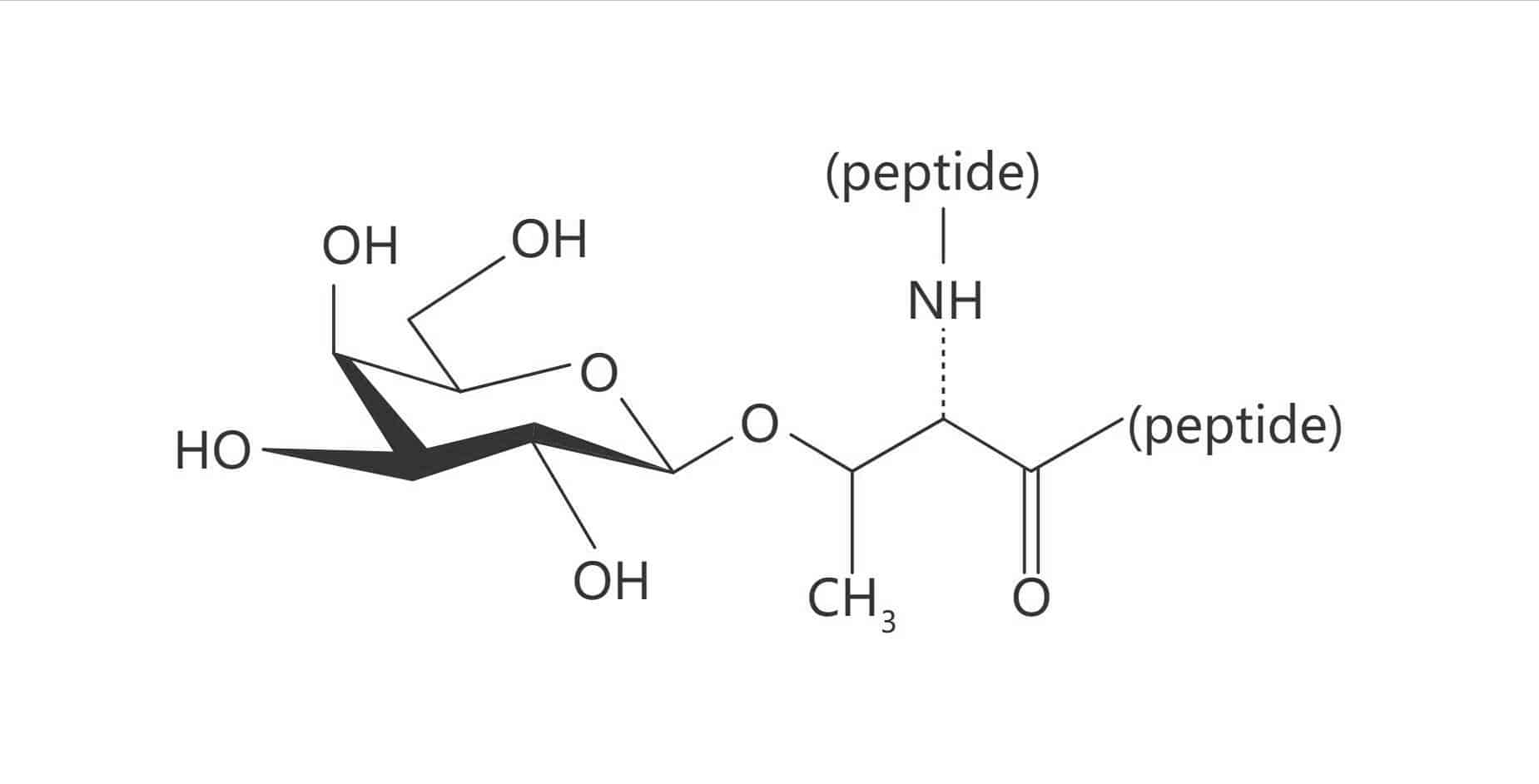
Ser(β-D-Gal)
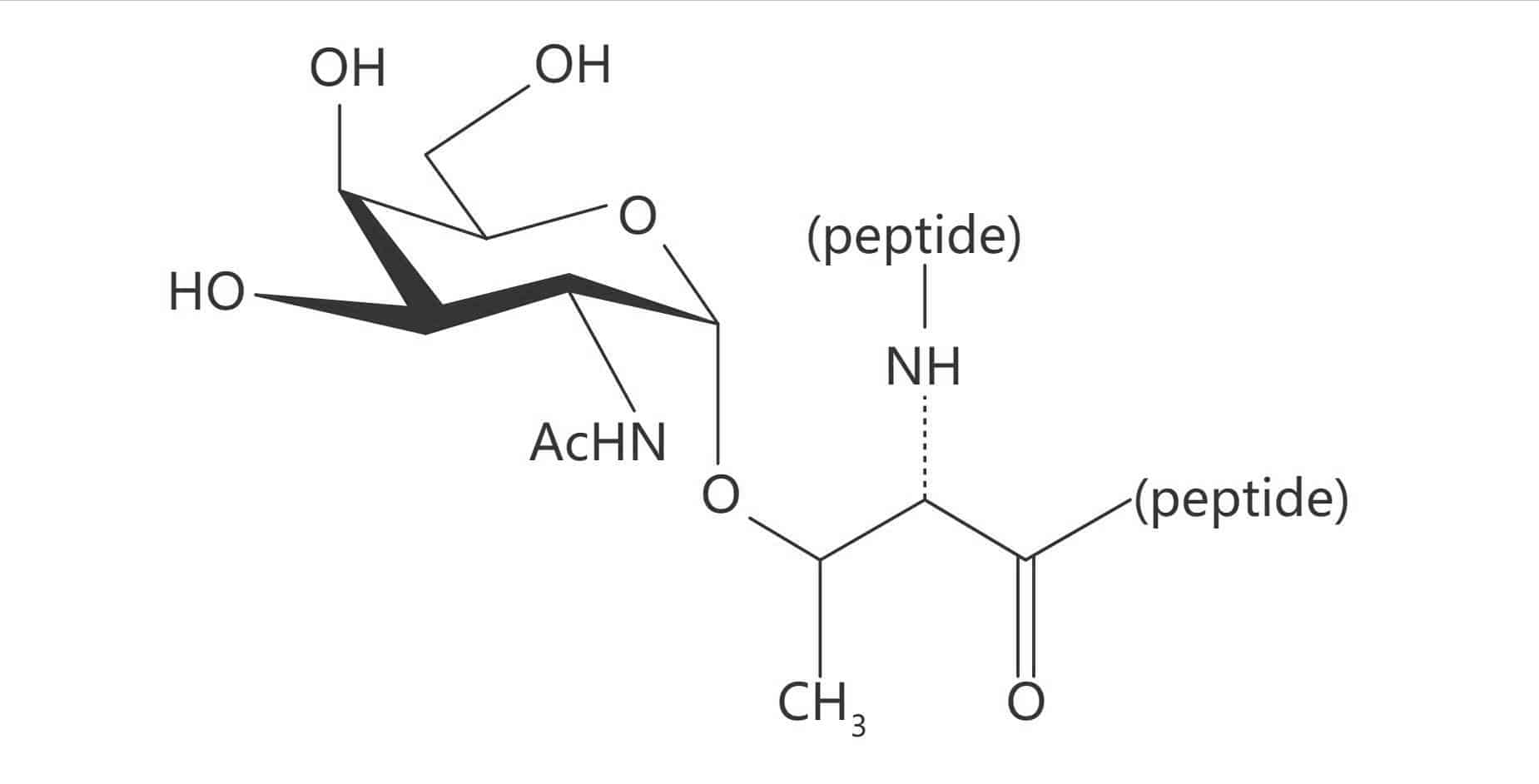
Thr(α-D-GalNAc)
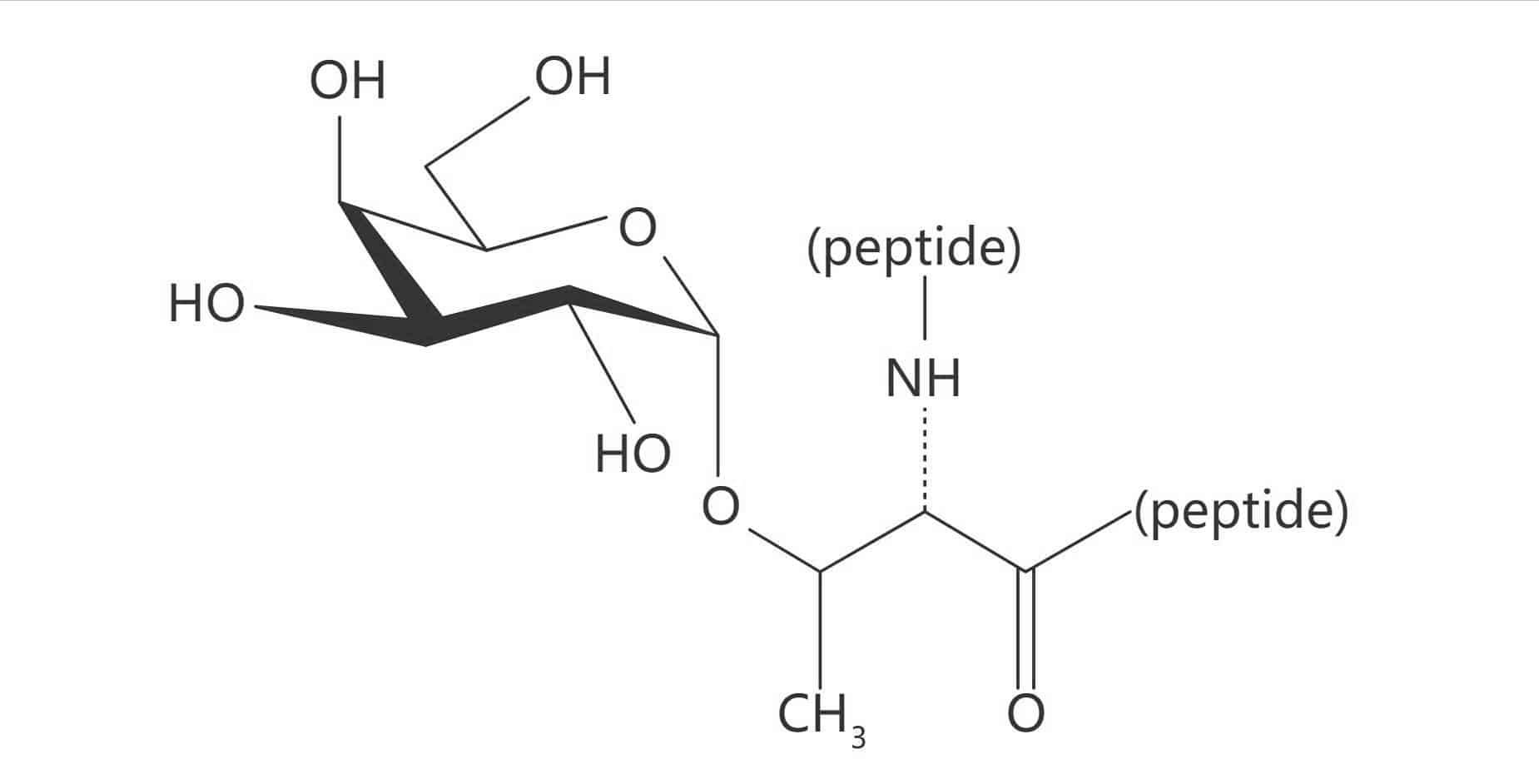
Thr(α-D-Gal)
Thr(Gal β(1-3) GalNAc)|(TF Antigen)
Thr(β-D-Gal)
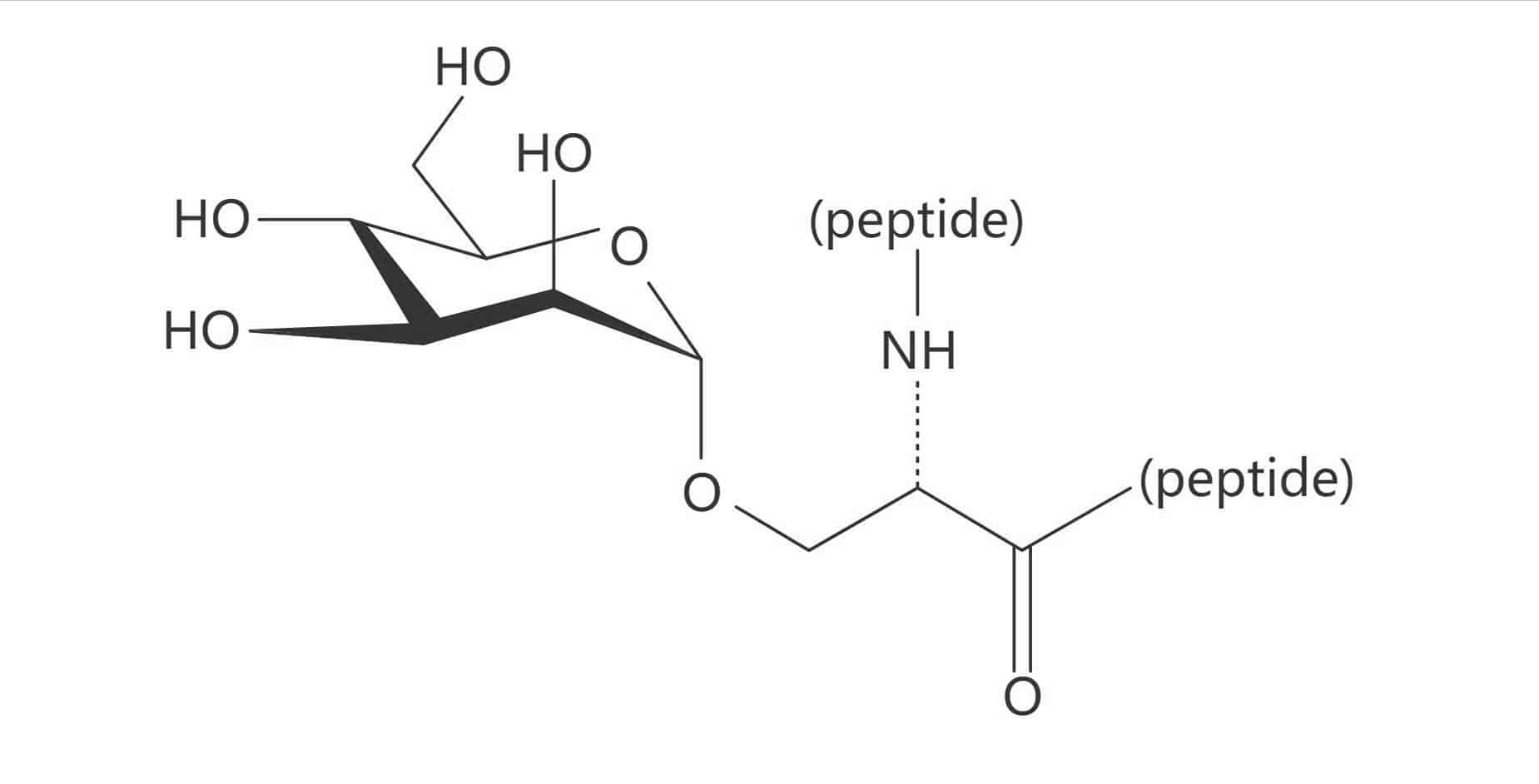
Mannose
Ser(α-D-Man)
Thr(α-D-Man)
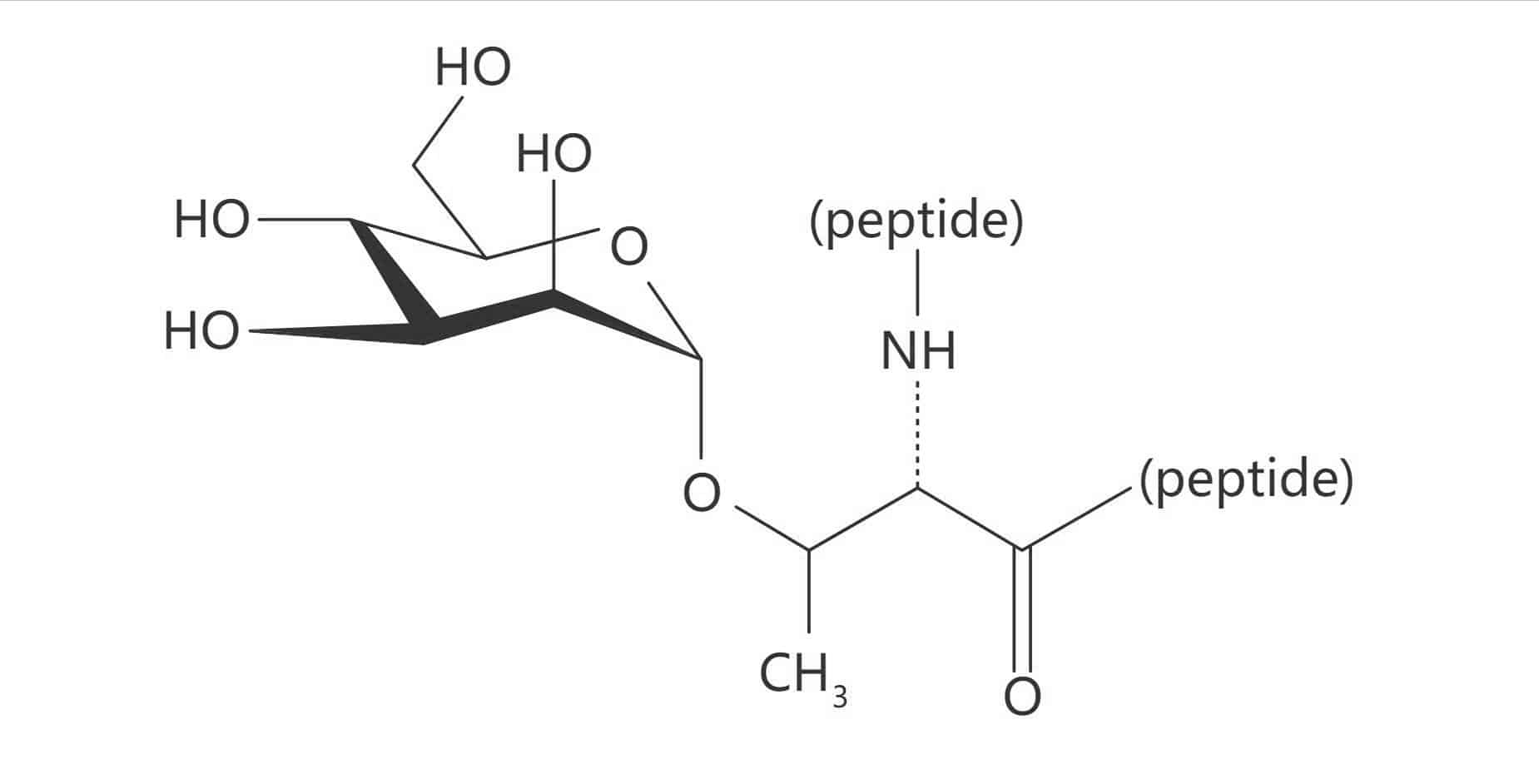
Glycated
Glycated Valine (Amadori Product)
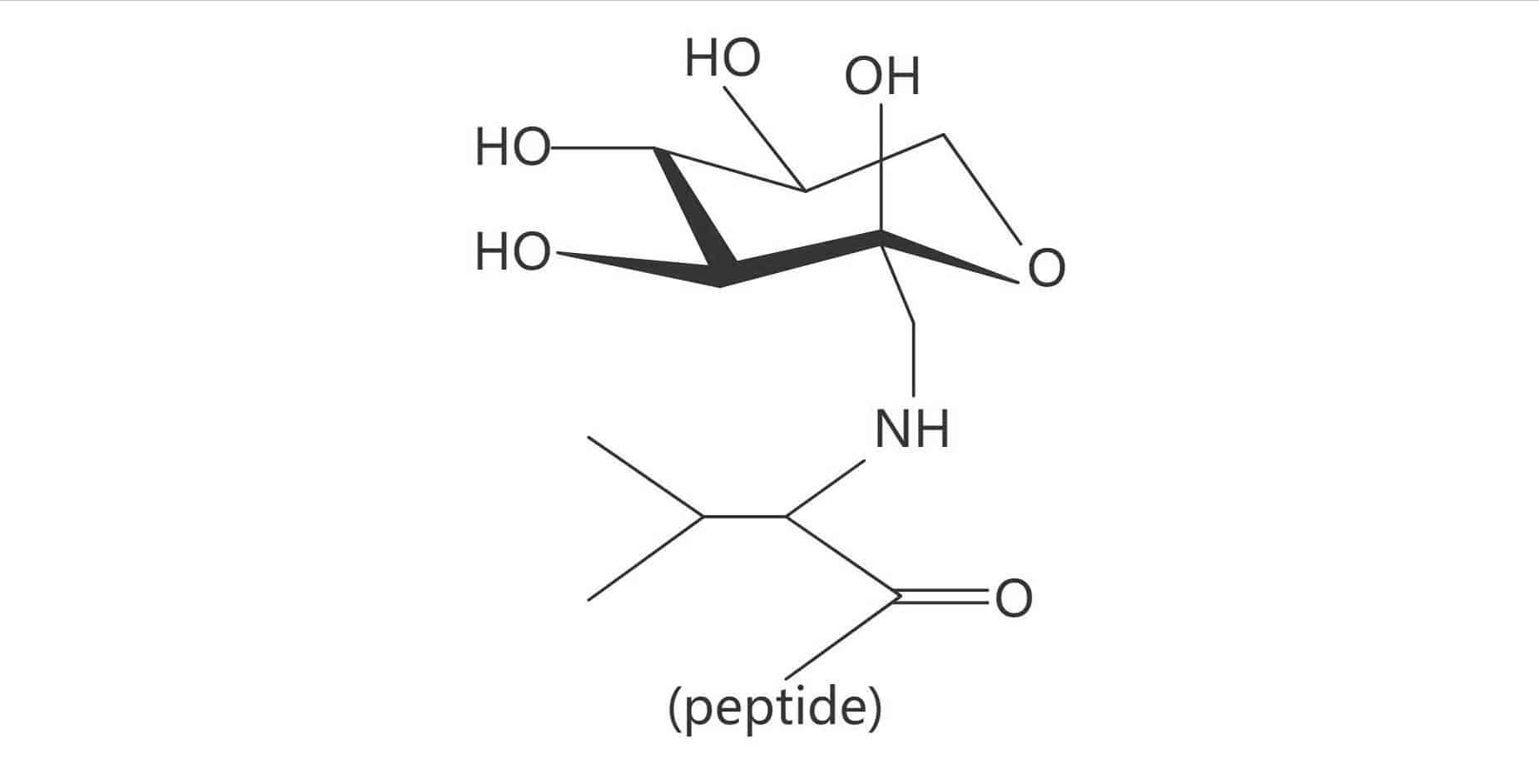
Importance of Glycosylation
The normal glycosylation occurs via enzymatic reaction in the body, it is imperative to the function of certain proteins. While glycation is referred to as a protein damage form, it is a non-enzymatic reaction. Glycosylation has critical role in physiochemical properties’ modulation of peptides and proteins, in order to the absorption through biological membranes.
Qyaobio provides the synthesis of glycopeptides and glycosylated peptides for worldwide researchers. We develop the glycosylated amino acids with standard protocols in Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). And apply the pre-synthesised glycosylated amino acids with SPPS to couple the elongating peptides. Our typical synthesis for peptides is 10-20 amino acids. It is difficult to synthesize long peptides more than 50 residues, because of the incomplete couplings and epimerization in integration.
QYAOBIO provides specific and unique peptide glycosylation service of monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide. Other glycosylation modifications of sialic acid, fucose are also performed on the main and side chain of polypeptide.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
